Small Running Title
The Neurobiology of Fear: Understanding Anxiety in Autism Spectrum disorder
Publication: Journal of Multiscale Neuroscience DOI: https://doi.org/10.56280/
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
How to cite this paper
Lleuvelyn A. Cacha, Dolores Mirabueno and Lourdes P. Terrado (2025) The Neurobiology of Fear: Understanding Anxiety in Autism Spectrum disorder. Journal of Multiscale Neuroscience 4(3), 196-206
DOI: https://doi.org/10.56280/
Author Affiliation
Graduate School
Research Coordination
University of the East, Manila
Dolores Mirabueno
College of St Benilde, De La Salle University
Lourdes P. Terrado
Graduate School
University of the East, Manila
Received 9 July 2025
Accepted 10 August 2025
Online published September 2025
Abstract
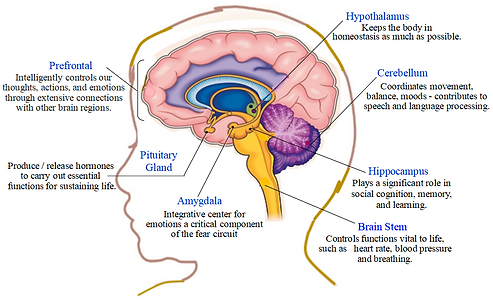
Autism spectrum disorder does not include anxiety as one of its core features, which has its own unique and additional level of complexity. The prevalence of anxiety disorder is not considered a core dimension , yet majority of individuals with autism exhibit clinically elevated levels of anxiety or suffer from at least one anxiety disorder, including obsessive-compulsive disorder. Individuals with anxiety are more susceptible to heightened and prolonged negative emotional states, which are indicative of potential dysfunctions within the brain systems responsible for regulating negative emotions. Anxiety is believed to have a neurobiological component, and considerable research has long been conducted to determine how its arousal impacts behavioral development in typical situations. Investigation has focused on the structural development of the amygdala implicated in the neurobiology of autism. An overview of the role of the prefrontal cortex in modulation of amygdala function is presented in this paper, as well how differences in amygdala and prefrontal cortex connectivity may play a role in influencing the presentation of anxiety syndrome in the context of autism spectrum disorder.
Keyword: Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), anxiety, amygdala, neural circuits, brain connectivity, functional connectivity, neural mechanisms, emotion regulation, anxiety pathways in autism
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Neural Press.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, Neural Press™ or the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

.png)