Volume 4 Issue 2 (June 2025)

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
R.R. Poznanski, O. Pusuluk and C.H.Raymond Ooi
This paper presents a theoretical model proposing that quasiparticle-mediated proton (H+) dynamics, modulated by dipolar excitations across π-conjugated organic molecules, specifically at amphipathic membrane proteins and interfaces, give rise to emergent hybrid modes—termed tripartite quasipolaritons—under nonequilibrium steady-state conditions. These modes arise from light-matter-vibration coupling dynamics. Quasiparticle-mediated proton dynamics within the hydrophobic pockets of amphipathic complexes occur through their non-closure under nonequilibrium steady-state conditions. We explore how quantum optical effects facilitate light-matter interactions, enhancing photoprotection, involving vibrational modes when anti-entropic conditions prevail for delocalized π-excitations while maintaining conserved epistemic quantum entropy. Dipolar excitations through patterns of energetic uncertainties play a role in establishing the conditions needed for a unified and interconnected informational system of photon pathways in aromatic amino acid residues. This system is proposed to link localized biochemical processes involving π-H+ interactions and π-π stacking of amino acids....
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Marco Cavaglià, Silvia Vernuccio and Jack Tuszynski
Cell membranes are highly complex biological systems composed of a wide array of lipid species, distributed asymmetrically across the bilayer leaflets. This highly specific lipid composition is essential for maintaining membrane integrity and functionality, yet simplified models are often used in molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Such simplifications might lead to inaccurate representations of the structural and functional characteristics of the membrane. In this study, we compare a generic mammalian membrane model with two brain-specific neuronal membrane models to assess the impact of lipid composition on simulation outcomes. By combining experimental data and earlier computational models, we developed consensus models representing the membrane of the neuronal soma and the synaptic plasma membrane, using lipids with readily available and validated molecular mechanics parameters in the CHARMM36 force field. MD simulations revealed distinct structural and mechanical properties in brain-specific membranes, including increased area ...


REVIEW
Integrative chronic pain management: a narrative review
Matthew Halma, Paul Marik, Yusuf Saleeby, Joseph Varon and Jack A. Tuszynski
Chronic pain, a pervasive public health issue, significantly contributes to the opioid crisis in the United States, where opioid-related deaths have escalated dramatically since the late 1990s. This narrative review explores integrative approaches to managing chronic pain, aiming to reduce reliance on opioid medications. It synthesizes evidence from randomized controlled trials, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews, focusing on various pain etiologies, including arthritis, musculoskeletal pain, postsurgical pain, cancer-related pain, fibromyalgia, migraines, and neuropathic pain. Key findings suggest that dietary interventions, lifestyle modifications, and complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, and photobiomodulation therapy, can significantly alleviate pain across multiple conditions. These integrative strategies not only manage pain but also address the pain epidemic and the opioid crisis by offering personalized, multimodal treatment plans that consider the complexity of chronic pain, its psychological and social determinants ....
PERSPECTIVE
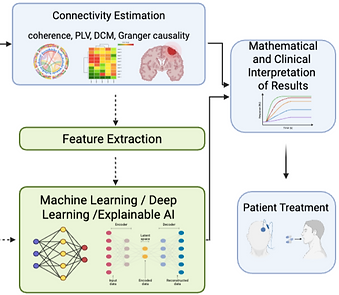
Investigating brain connectivity from a signal processing perspective
Alexandra Tsipourakis and Marco Agostino Deriu
Understanding brain connectivity is crucial for deciphering both neural function and dysfunction. This review highlights the key signal-processing methods used to analyze brain connectivity, including techniques such as Fourier transforms, wavelet analysis, and graph-theoretical approaches. Applications of these techniques across neuroimaging and electrophysiological modalities such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) are examined. Additionally, challenges such as noise reduction, signal non-stationarity, and computational complexity are addressed. By bridging neuroscience and signal processing, this review aims to provide insights into the strengths and limitations of both traditional and cutting-edge signal-processing methods for studying brain connectivity while also highlighting potential future research directions.

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Analyzing neonatal vocal expression: Methodological approaches to identifying neurological and psychiatric signatures
Syed Taimoor Hussain Shah, Syed Adil Hussain Shah, Andrea Buccoliero, Iqra Iqbal Khan, Syed Baqir Hussain Shah, Angelo Di Terlizzi, & Giacomo Di Benedetto
Understanding the complexity of brain organization and connectivity is a key step in elucidating the functioning of our brains, including aspects such as consciousness, perception, or thought. Some information about this complexity could be encoded and compressed into distinctive personal characteristics, such as voice, which can serve as a true neurobiological “fingerprint.” In this connection, analyzing infant vocalization patterns offers a unique opportunity to explore neurodevelopmental trajectories and sensory integration. Understanding how this information is encoded in vocal expression could help us determine new biomarkers filled with information about how our brains function, relevant to neurodevelopment. Despite significant advances in neonatal care, accurately identifying neurological and cognitive signatures from infant vocalizations remains a profound challenge, as it requires bridging multiscale brain dynamics with perceptual...
BRIEF REPORT
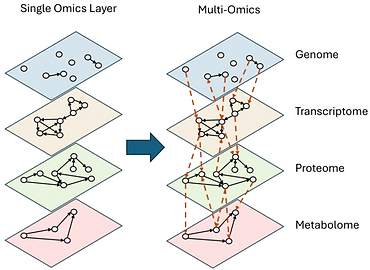
Molecular Biomarker Discovery Targeting Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Cognitive Mechanisms
Konstantinos Panagiotopoulos and Marco Agostino Deriu
Brain disorders, which encompass neurodevelopmental conditions and age-related neurodegenerative diseases, are becoming more prevalent due to population growth, increased life expectancy, and enhanced diagnostic capabilities. Despite clinical differences, these diseases share complex molecular alterations: dysregulation of coding and noncoding RNAs, epigenetic modifications, and altered protein networks. Today, we can directly quantify those alterations. However, determining their relationship to brain function and identifying characteristic disease patterns through the integration of these biomarkers remains a significant challenge. Bioinformatics has become key to understanding these signals, helping us interpret what they tell us about the mechanisms that regulate our physiology and its pathological changes through multi-omics data integration. By analyzing the interplay between genetic, transcriptomic, and epigenetic factors, we can reconstruct disease-specific pathways and find potential links between early stages of brain development and degenerative processes.

.png)